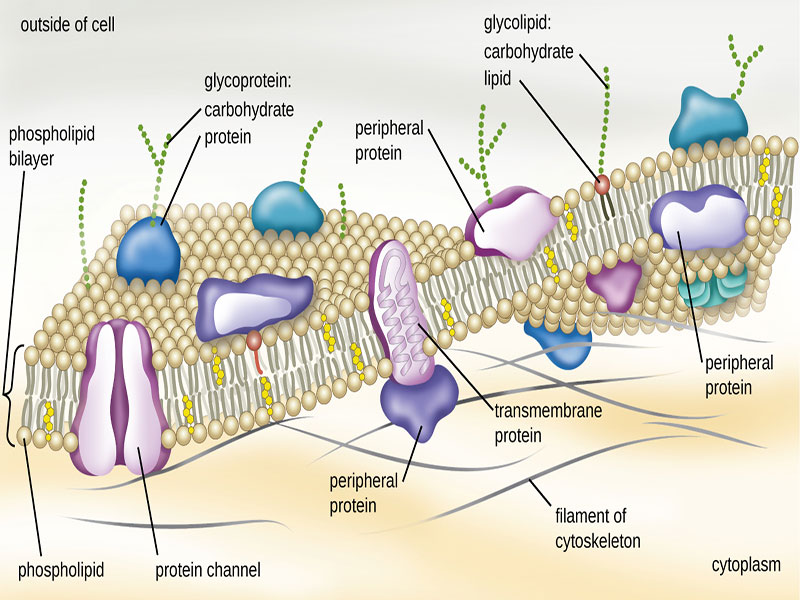
In fact the cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable that surrounds a cytoplasm of cell. It’s function that protect the integrity of the interior of the cell letting some materials keeping into cells. It also serves as a base of interest for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others. Thus the cell membrane serves to help support the cell and help keeping its form. One of functions of membrane is to set cell growth through the balance of exocytosis and endocytosis. In endocytosis, proteins and lipids are eliminated from the cell membrane as materials are internalized. In exocytosis, containing lipids and proteins fuse with the cell membrane increasing cell size. Prokaryotic cells, fungal cells, animal cells and plant cells have plasma membranes. Internal organelles are coated by membranes.
Cell membrane structure
The cell membrane is composed of a mix of lipids and proteins. Lipids can exist in membrane and lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane with proteins. Lipids helped to membrane until have flexibility and proteins maintain the cell’s chemical climate and helped to membrane until transfer of molecules across the membrane.
Cell membrane lipids
Phospholipids are main and major component of cell membrane. Phospholipid form a lipid bilayer in which hydrophilic (we called that attracted to water) head areas automatically arrange to face the extracellular fluid and the aqueous cytosol, while their hydrophobic (we called that repelled by water) tail areas face away from extracellular fluid and cytosol. The lipid bilayer is semi permeable letting only certain molecules to spread across the membrane.
Cholesterol is another components of membrane. Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed in between membrane phospholipids. This supported keep cell membrane from becoming horny by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol isn’t existed in plant membrane. Glycolipids are existed on cell membrane surfaces and they have a long tail is carbohydrates sugar chain linked them. They support and help cells to identify other cells of the body.
Cell membrane proteins
Cell membrane has two type of proteins. Peripheral membrane proteins are exist out of membrane cell and help to connected membrane by interaction with other proteins. Integral membrane proteins are concatenated into the cell membrane and most of these proteins cross the membrane. Sections of these transmembrane proteins are subjected on both sides of the membrane. Cell membrane has many different functions. Structural proteins help to give shape and support the cell. Receptor proteins in cell membrane helps cell linking and communication with their external environment until cell could use hormones, neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules.
Transport proteins such as globular proteins and transport molecules across cell membranes through comforted diffusion. Glycoproteins have a carbohydrate chain pasted to them. They are embedded in the cell membrane and help in cell to molecule transport across the membrane and cell communications.
Organelle Membranes
Some cell organelles are surrounded by protective membrane. For instance the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, vacuoles and Golgi apparatus are samples of membrane-bound organelles. Mitochondria and chloroplasts surrounded by a double membrane. The membranes of the different organelles alter in molecular combination and are well suitable for the functions they make. Organelle membranes are played important and vital roles in cells functions including cellular respiration, lipid production and protein synthesis.
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
The cell membrane is one of the components of cell that protect the cell. Structural cell can exist in animal eukaryotic cell:
* Centrioles: help to arrange the assembly of microtubules.
* Chromosomes: house cellular DNA. This structure exist in nucleus.
* Cilia and Flagella: help to cellular movement.
* Endoplasmic reticulum: produces lipids and carbohydrates.
* Golgi Apparatus: the organelles that produces, stores and ships certain cellular products.
* Lysosomes: digest macromolecules in cells.
* Mitochondria: provide energy for the cell.
* Nucleus: controls cell growth, replicate and breed.
* Peroxisomes: one of components that digested organic materials in cell that digested organic material.
* Ribosomes: this structure has responsibility about protein production through translation.
Source link: https://www.thoughtco.com/cell-membrane-373364